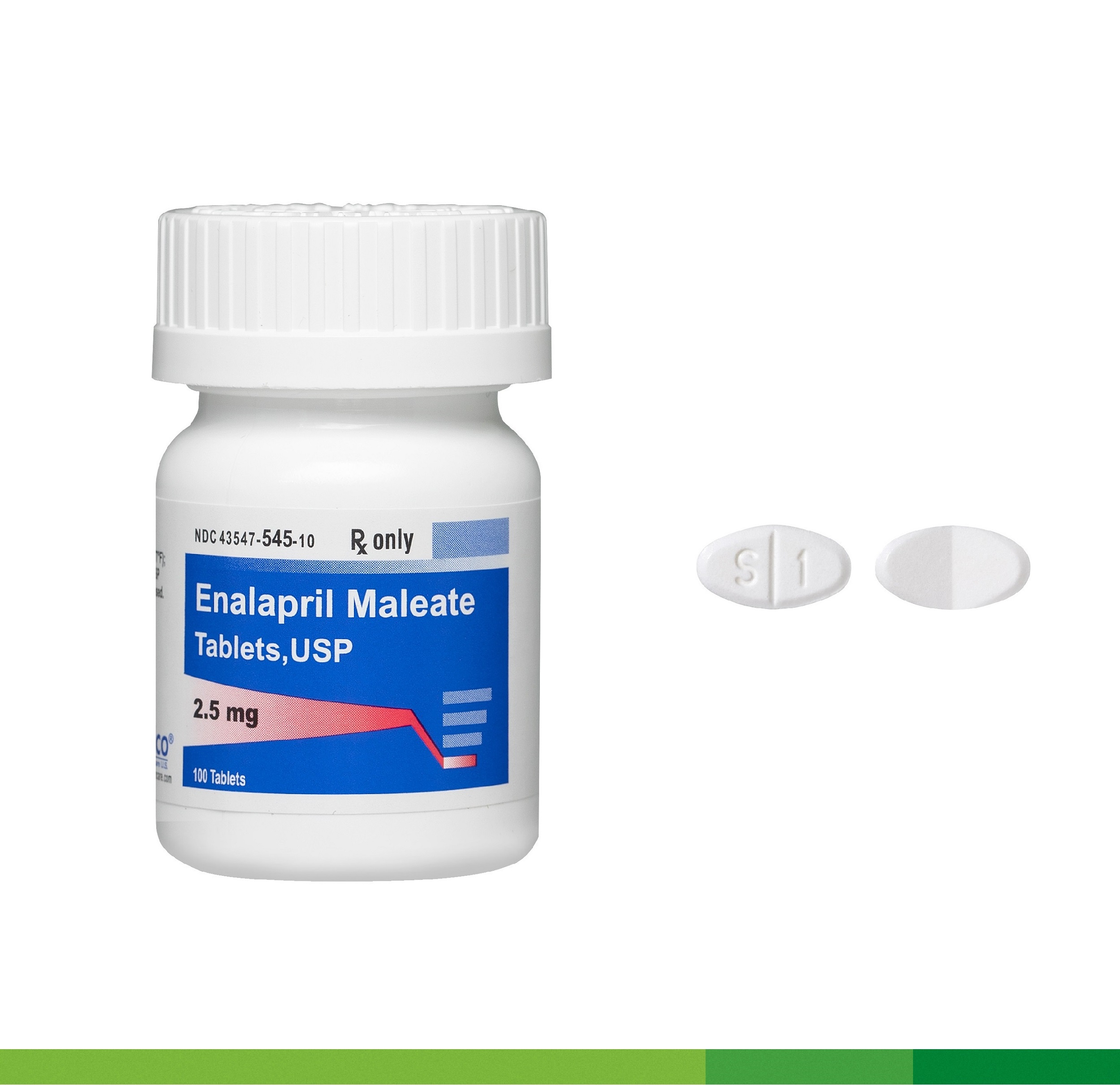
Consider incorporating Enalapril tablets into your daily routine if you are managing high blood pressure. This medication works by relaxing blood vessels, which lowers blood pressure and enhances blood flow. It’s particularly effective for individuals dealing with conditions like heart failure or chronic kidney disease.
When taking Enalapril, adhere to your healthcare provider’s dosage recommendations. Often prescribed once daily, the tablets can be ingested with or without food. Regular monitoring of blood pressure will ensure that the drug is working effectively. If you experience sudden side effects such as dizziness or swelling, consult your doctor promptly.
While Enalapril is generally well-tolerated, understanding possible interactions with other medications is crucial. Make sure to inform your healthcare provider about any additional prescriptions or over-the-counter drugs you are using. Staying informed about your treatment and discussing any concerns can enhance your experience with this medication.
- Comprehensive Guide to Enalapril Tablets
- Understanding the Mechanism of Action of Enalapril
- Indications and Dosage Recommendations for Enalapril
- Dosage in Special Populations
- Monitoring and Adjustments
- Potential Side Effects and Interactions of Enalapril Tablets
- Drug Interactions
- Monitoring and Management
- Guidelines for Safe Use and Patient Monitoring on Enalapril
- Initial Dosage and Adjustments
- Regular Assessments
- Patient Education
Comprehensive Guide to Enalapril Tablets
Take Enalapril tablets as prescribed by your healthcare provider to manage high blood pressure and heart failure. This medication belongs to the class of ACE inhibitors, which work by relaxing blood vessels, promoting better blood flow. Regular monitoring of blood pressure helps assess the medication’s effectiveness.
Administer Enalapril orally, typically once or twice daily, with or without food. Consistent timing enhances adherence to the treatment plan. If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it’s close to the next dose, skip the missed dose and return to your regular schedule. Avoid taking double doses.
Common side effects include dizziness, fatigue, and a dry cough. Report persistent or severe symptoms to your doctor. Serious side effects may involve swelling of the face, lips, or throat, requiring immediate medical attention. Monitor your potassium levels as Enalapril may increase potassium retention.
Stay hydrated and avoid excessive potassium supplements unless directed by your healthcare professional. Be cautious with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) as they may hinder the medication’s efficacy. Discuss all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, with your doctor to prevent interactions.
Evaluate your kidney function regularly through blood tests as Enalapril can affect renal health. If you have a history of renal issues, your doctor may adjust your dosage accordingly. Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should consult a healthcare provider before using Enalapril, as it may pose risks to the fetus or infant.
Engage in lifestyle modifications alongside medication, such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight. These changes contribute to better management of blood pressure and overall cardiovascular health. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider ensure effective management of your condition while using Enalapril tablets.
Understanding the Mechanism of Action of Enalapril
Enalapril functions primarily as an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. It decreases the production of angiotensin II, a peptide that constricts blood vessels and raises blood pressure. By inhibiting ACE, enalapril promotes vasodilation, leading to reduced blood pressure and improved blood flow.
Enalapril also helps in lowering blood volume by decreasing aldosterone secretion. Aldosterone typically prompts the kidneys to retain sodium and water; by inhibiting this process, enalapril facilitates the excretion of excess sodium and fluid. The reduction in blood volume contributes to further lower blood pressure levels.
This medication is particularly beneficial for individuals with hypertension or heart failure. It alleviates the heart’s workload by lowering resistance in the blood vessels, allowing the heart to pump more efficiently. Moreover, enalapril aids in improving renal function by enhancing blood flow to the kidneys, especially in patients with conditions like diabetes.
Regular monitoring of blood pressure and kidney function can ensure the optimal use of enalapril, making adjustments as necessary based on individual responses. Always consult with a healthcare provider before making any changes to medication regimens.
Indications and Dosage Recommendations for Enalapril
Enalapril is indicated for the treatment of hypertension and heart failure. This medication helps lower blood pressure and reduce the workload on the heart. For adults with hypertension, the typical starting dose is 5 mg once daily. Depending on the patient’s response, the dose may be adjusted, with a maximum recommended dose of 40 mg per day.
Dosage in Special Populations
Patients with renal impairment should receive careful dose adjustments. Start with a lower dose of 2.5 mg once daily and monitor blood pressure closely. For patients over 65, consider initiating treatment at 2.5 mg daily as well to minimize the risk of hypotension. In cases of heart failure, begin with 2.5 mg once or twice daily, titrating as needed based on the patient’s clinical response.
Monitoring and Adjustments
Regular monitoring of renal function and electrolytes is essential after starting Enalapril, especially in individuals with significant pre-existing kidney issues. Adjustments should be made based on blood pressure readings and patient tolerance to therapy.
Potential Side Effects and Interactions of Enalapril Tablets
Patients taking Enalapril tablets should monitor for several potential side effects. Common issues include dizziness, headache, and fatigue, primarily due to the medication’s effects on blood pressure. A relatively lower but serious concern involves angioedema, which presents as swelling of the face, lips, or throat. Immediate medical attention is crucial in such cases. Additionally, patients may experience a persistent dry cough, which can be bothersome and may require dosage adjustments or medication changes.
Drug Interactions
Enalapril can interact with various medications, leading to increased risks or reduced efficacy. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, may diminish the antihypertensive effects of Enalapril. Diuretics can enhance the blood-pressure-lowering effect, necessitating careful blood pressure monitoring. Combining Enalapril with potassium-sparing diuretics or potassium supplements can lead to hyperkalemia, a dangerous increase in potassium levels. Always consult a healthcare provider prior to initiating new medications or supplements while using Enalapril.
Monitoring and Management
Regular monitoring of renal function and electrolytes is crucial for those on Enalapril. Routine blood tests can help detect abnormalities early and allow for timely interventions. Inform your doctor of any side effects experienced to tailor the treatment plan effectively. Following these guidelines ensures safe and effective use of Enalapril tablets.
Guidelines for Safe Use and Patient Monitoring on Enalapril
Monitor blood pressure regularly during treatment with Enalapril. Aim for target levels as determined by your healthcare provider.
Initial Dosage and Adjustments
- Start with a low dose, typically 5 mg once daily for adults.
- Adjust the dosage based on blood pressure response and tolerance.
- Maximum daily dose can reach up to 40 mg, divided into one or two doses.
Regular Assessments
- Check kidney function through serum creatinine and potassium levels before starting therapy and periodically thereafter.
- Evaluate the presence of side effects, particularly cough or angioedema.
- Monitor for signs of hypotension, especially after the first dose or following dose increases.
Stay hydrated and avoid dehydration, which can increase the risk of low blood pressure and kidney problems.
Patient Education
- Inform patients about potential side effects and when to seek medical attention.
- Encourage adherence to prescribed dosages and schedules.
- Discuss lifestyle changes that may enhance therapeutic outcomes, such as diet and exercise.