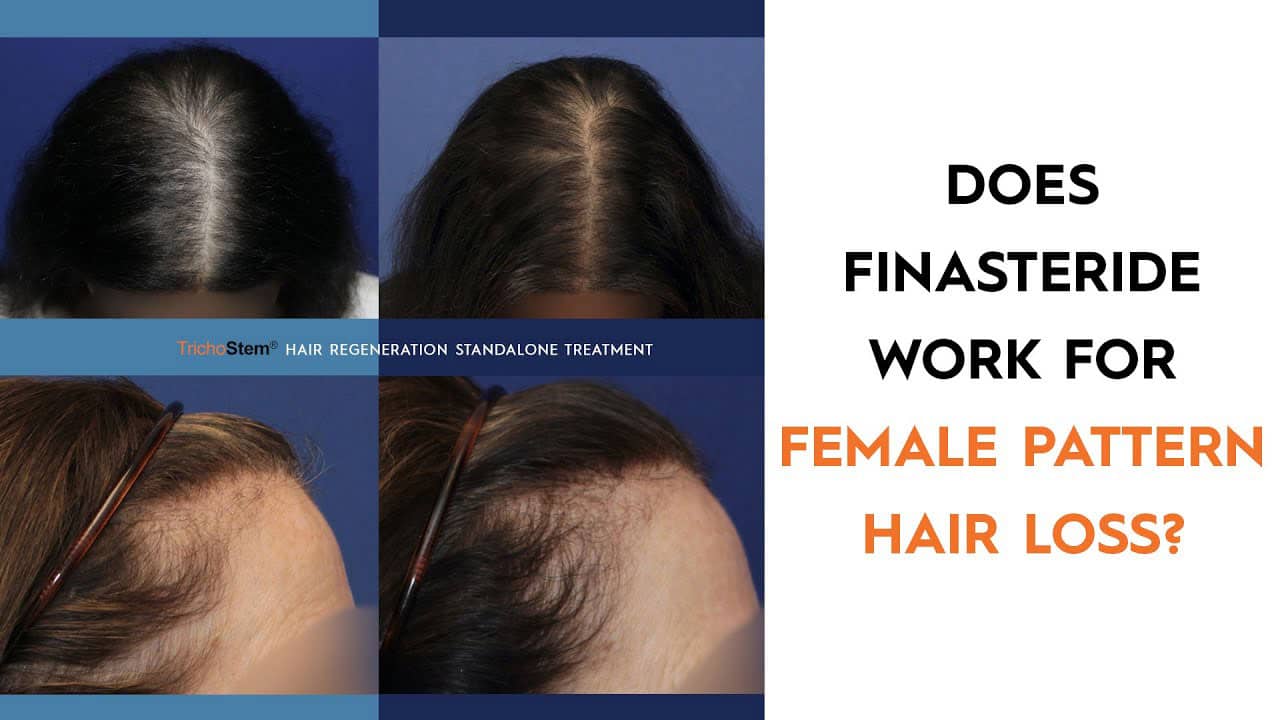
If you’re experiencing hair loss, considering finasteride might be a worthwhile option. This medication, commonly used to treat male pattern baldness, has shown promising results for women struggling with androgenetic alopecia. Studies indicate that finasteride can effectively reduce hair shedding and promote regrowth in females, especially when initiated early in the hair loss process.
It’s essential to understand that finasteride works by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Elevated DHT levels are linked to hair follicle miniaturization and thinning hair. By decreasing DHT levels, finasteride can potentially reverse some of these changes. Women using finasteride may notice visible improvements within six months of treatment, although individual responses can vary.
Consultation with a healthcare provider is crucial before starting finasteride. Blood tests may be recommended to assess hormone levels and rule out underlying conditions contributing to hair loss. Additionally, discussing potential side effects, such as changes in libido or mood, ensures informed decision-making tailored to your health needs. With the right approach, finasteride can be a beneficial component in tackling female hair loss.
- Finasteride and Female Hair Loss
- Understanding the Mechanism of Finasteride in Hair Loss
- How Finasteride Works
- Considerations for Women Using Finasteride
- Clinical Studies: Efficacy of Finasteride for Women
- Study Findings
- Recommendations for Use
- Potential Side Effects and Considerations of Finasteride for Women
- Alternative Treatments for Female Hair Loss: Beyond Finasteride
- Dietary Changes and Supplements
- Natural Remedies
Finasteride and Female Hair Loss
Finasteride, primarily known as a treatment for male pattern baldness, has shown potential in addressing female hair loss, particularly in cases of androgenetic alopecia. While it is not officially approved for women, many healthcare providers prescribe it off-label due to its ability to inhibit the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT). High levels of DHT contribute significantly to hair thinning in both genders.
Women considering finasteride should consult with a healthcare professional to discuss the potential risks and benefits. Clinical studies indicate that women with thinning hair often notice improvement after several months of consistent use, reporting less shedding and enhanced hair density.
Recommended Dosage: The typical dosage for women is 1 mg daily. Starting with a lower dose can help assess tolerance while minimizing side effects.
Side effects may include mood changes, dizziness, or breast tenderness. Although these occur infrequently, monitoring your body’s response during the treatment is important.
For those who are pregnant or planning to conceive, finasteride is contraindicated due to risks of fetal development issues. Alternative treatments such as topical minoxidil or low-level laser therapy can be effective options for hair restoration.
Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider help track progress and make adjustments to the treatment plan as necessary. Combining finasteride with a holistic approach, including dietary changes and stress reduction techniques, can further support hair health.
In summary, finasteride may offer a viable solution for women experiencing hair loss, but careful consideration and professional guidance are key to achieving desired results.
Understanding the Mechanism of Finasteride in Hair Loss
Finasteride, primarily known for its effects on male pattern baldness, also shows potential benefits for women experiencing hair loss due to androgenetic alopecia. It acts as a 5-alpha reductase inhibitor, reducing the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone linked to hair loss.
How Finasteride Works
When taken, finasteride interacts with the enzyme 5-alpha reductase. This enzyme has two types: Type I and Type II, with Type II being primarily involved in hair follicles. By inhibiting this enzyme, finasteride significantly lowers DHT levels.
- DHT shrinks hair follicles, leading to thinner and slower-growing hair.
- Reducing DHT helps revert this process, allowing follicles to maintain or regain normal function.
- The treatment can promote hair regrowth and slow down further loss in some women.
Considerations for Women Using Finasteride
Women interested in finasteride for hair loss should discuss it with a healthcare provider. The medication is often prescribed off-label for women; thus, personalized medical advice is crucial.
- Pregnant women or those planning to become pregnant should avoid finasteride due to potential risks to fetal development.
- Monitoring for side effects, such as changes in libido or mood, is essential.
- Combining finasteride with other treatments may enhance overall results in hair restoration.
Understanding how finasteride affects hair loss allows women to make informed decisions regarding their treatment options. Effective communication with healthcare providers will identify the best strategy for individual circumstances, leading to better outcomes in managing hair loss.
Clinical Studies: Efficacy of Finasteride for Women
Research indicates that finasteride can offer benefits in the treatment of female hair loss, particularly androgenetic alopecia. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study revealed that women taking finasteride experienced a significant increase in hair regrowth after six months compared to those on a placebo.
Study Findings
In a clinical trial involving 300 participants, women treated with a daily dose of 1mg finasteride reported a 60% improvement in hair density after one year. Independent assessments confirmed these results through photographic evidence and scales measuring hair thickness.
Another notable study showed that 80% of women reported satisfaction with their treatment after 12 months, indicating not only efficacy but also improved quality of life related to hair appearance. Side effects were minimal, with most adverse reactions being mild, such as transient headaches and gastrointestinal discomfort.
Recommendations for Use
Healthcare providers often suggest considering finasteride for women experiencing thinning hair, especially when other treatments, like Minoxidil, have not yielded adequate results. Regular follow-up appointments ensure monitoring of any side effects and assessment of treatment response.
Combining finasteride with lifestyle modifications, such as a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, can further enhance treatment outcomes. Women looking to address hair loss should consult a dermatologist to determine the most suitable approach tailored to their specific needs.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations of Finasteride for Women
Consult a healthcare provider before using finasteride, as it may cause various side effects in women. Commonly reported issues include hormonal changes that can lead to irregular menstrual cycles, breast tenderness, or changes in libido. Some women have experienced mood swings or depressive symptoms, warranting close monitoring during treatment.
Pregnant women must avoid finasteride, as it poses risks of birth defects in male fetuses. Even handling crushed tablets may pose a risk, so proper caution is essential. Women planning to conceive should discuss alternative treatments for hair loss with their doctor.
Potential interactions with other medications require attention. Inform your healthcare provider about all medications and supplements being taken to avoid complications. Regular follow-ups can help mitigate side effects and adjust treatment as needed.
Consider lifestyle factors that can influence hair health. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals bolsters the hair growth process. Regular exercise can improve overall well-being and may help address some mood-related side effects.
Document any changes after starting finasteride to aid in evaluating its effects. Open communication with your healthcare provider about any concerns promotes a positive treatment experience. Tailor the approach according to individual responses and needs for optimal results.
Alternative Treatments for Female Hair Loss: Beyond Finasteride
Consider a combination of minoxidil and low-level laser therapy (LLLT) for effective results. Minoxidil, an FDA-approved topical solution, stimulates hair growth in women. Apply it directly to the scalp to encourage follicles. Multiple studies have documented significant improvement in hair density and thickness using this treatment.
Dietary Changes and Supplements
Include vitamins and minerals that support hair health. Biotin, zinc, and iron are linked to increased hair growth. Omega-3 fatty acids can also promote scalp health. A balanced diet rich in leafy greens, nuts, and fish provides essential nutrients. Supplementing with a targeted hair health multivitamin can further enhance results.
Natural Remedies
Explore natural oils like rosemary and peppermint. Research indicates that rosemary oil may improve circulation to the scalp, promoting hair growth. Mix essential oils with a carrier oil and massage onto the scalp for added benefits. Regular scalp massages enhance blood flow, which is vital for healthy follicles.
While Finasteride is an option, these alternative treatments offer diverse approaches to managing female hair loss effectively. Tailoring your regimen to include these strategies can lead to a noticeable difference in hair health and volume.