If you’re dealing with prostate inflammation, considering finasteride as a treatment option might be beneficial. This medication has shown effectiveness in reducing the size of an enlarged prostate, thereby alleviating discomfort associated with inflammation. By lowering levels of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), finasteride addresses one of the underlying causes of prostate issues.
Research indicates that finasteride can significantly improve urinary symptoms related to prostate inflammation. Many patients report a decrease in urgency, frequency, and pain during urination after starting treatment. For optimal results, consult with a healthcare provider to tailor a personalized approach based on your specific situation.
In addition to medication, lifestyle changes can enhance the benefits of finasteride. Regular physical activity, a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, and staying hydrated contribute positively to prostate health. Combining these strategies with finasteride treatment can lead to improved outcomes and increased comfort.
Regular follow-ups with your healthcare professional are crucial to monitor progress and adjust treatment as necessary. Taking proactive steps in the management of prostate inflammation can lead to a significant improvement in quality of life. With the right approach, you can successfully navigate this aspect of health and wellness.
- Finasteride and Prostate Inflammation: An Informative Guide
- Understanding Prostate Inflammation
- Symptoms and Diagnosis
- Treatment Options
- Mechanism of Action of Finasteride
- Clinical Applications of Finasteride for Prostate Issues
- Potential Side Effects of Finasteride in Prostate Inflammation Treatment
- Less Common Side Effects
- Monitoring Recommendations
- Comparative Effectiveness of Finasteride vs. Alternative Treatments
- Recommendations for Patients Considering Finasteride
Finasteride and Prostate Inflammation: An Informative Guide
Finasteride, commonly used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and male pattern baldness, has gained attention for its potential impact on prostate inflammation. Clinical studies indicate that finasteride can reduce prostate size and alleviate symptoms related to prostate inflammation, particularly in men with BPH.
Dosage plays a significant role in the effectiveness of finasteride. The typical dose for BPH is 5 mg daily. Adhering to this dosage can lead to noticeable improvements in urinary flow and reduced discomfort associated with prostate issues.
Side effects, while they occur in some patients, vary in severity. Commonly reported issues include decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and mood changes. Monitoring these side effects with a healthcare provider ensures adjustments can be made if necessary.
Combining finasteride with other treatments may enhance its effects. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help address inflammation directly, while lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, support overall prostate health. Incorporating foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants can further benefit inflammation reduction.
Regular follow-ups with a healthcare professional are crucial. These check-ins allow for assessment of both progress and any adverse effects from the medication. A tailored treatment plan can maximize benefits while minimizing risks.
In summary, finasteride presents a viable option for managing prostate inflammation, particularly related to BPH. Understanding its benefits, side effects, and interaction with other treatments can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their prostate health.
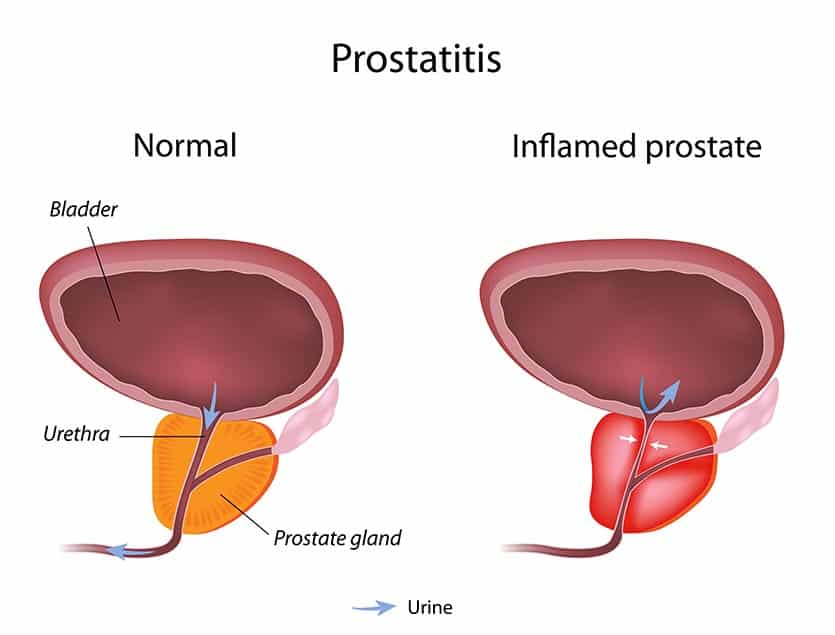
Understanding Prostate Inflammation
Prostate inflammation, or prostatitis, frequently affects men, causing discomfort and urinary issues. Recognizing its types is fundamental: acute bacterial prostatitis, chronic bacterial prostatitis, chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome, and asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis. Each category has distinct causes and treatment approaches.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms can include pain during urination, difficulty urinating, frequent urge to urinate, and pelvic pain. A healthcare professional may perform a physical examination, including a digital rectal exam (DRE), and may recommend tests such as urine analysis or cultures to determine the presence of infection.
Treatment Options
Management strategies vary based on the prostatitis type. For bacterial cases, antibiotics are often prescribed. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may alleviate pain. Lifestyle modifications, including increased hydration and regular exercise, can also provide relief. Finasteride is sometimes utilized, particularly in cases of benign prostatic hyperplasia, to reduce prostate size and its associated symptoms.
Implementing these strategies can significantly enhance quality of life for individuals suffering from prostate inflammation. Always consult a healthcare professional for tailored advice and treatment plans to address this condition effectively.
Mechanism of Action of Finasteride
Finasteride inhibits the 5-alpha-reductase enzyme, which converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT). By blocking this conversion, finasteride effectively reduces DHT levels in the body. DHT is known to contribute to prostate inflammation and enlargement, thus managing symptoms associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Lowering DHT levels results in decreased cellular proliferation in the prostate, leading to a reduction in its size. This mechanism alleviates urinary symptoms, making it easier for patients to urinate and improving overall urinary flow.
Finasteride’s action also extends to hair follicles. In individuals experiencing androgenetic alopecia, reduced DHT helps to slow hair loss and may encourage regrowth. This dual benefit highlights the drug’s versatility in addressing both prostate and hair-related issues.
Regular use over several months is necessary to observe significant effects. Frequent monitoring and consultation with healthcare providers ensure that the treatment aligns with patient needs and minimizes potential side effects.
In summary, finasteride’s primary function lies in its ability to inhibit 5-alpha-reductase, leading to decreased DHT levels, which subsequently benefits prostate health and hair growth processes.
Clinical Applications of Finasteride for Prostate Issues
Finasteride is widely used for managing prostate conditions, specifically benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and male pattern baldness. Its ability to inhibit the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) makes it a valuable option in clinical settings.
For patients with BPH, finasteride significantly reduces prostate size, alleviating urinary symptoms. Studies indicate that it can improve urinary flow and decrease the risk of acute urinary retention. A treatment course may last 6-12 months to maximize results.
When considering finasteride for prostate inflammation, monthly evaluations help monitor patient response. Typical dosing starts at 5 mg daily. Alongside medication, integrating lifestyle changes proves beneficial. These include:
- Maintaining a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables
- Engaging in regular exercise to improve overall health
- Avoiding excessive alcohol and caffeine intake
Additionally, several studies show that finasteride can lower the risk of prostate cancer, particularly high-grade tumors. The FDA acknowledges this benefit, enhancing its appeal among urologists.
For those experiencing adverse effects, common ones include sexual dysfunction and breast tenderness. Discussing potential side effects with patients ensures informed decision-making while they weigh the benefits against risks.
Regular follow-ups are crucial for patients on finasteride. Monitoring PSA levels allows healthcare professionals to assess treatment effectiveness while establishing a baseline. Adjustments to the dosage may be necessary based on individual responses.
In conclusion, finasteride offers notable benefits for patients with various prostate issues. Medical providers frequently recommend it as part of a comprehensive management plan, considering each patient’s unique circumstances and health profile.
Potential Side Effects of Finasteride in Prostate Inflammation Treatment
When using Finasteride for prostate inflammation treatment, awareness of potential side effects is key. Commonly reported effects include sexual dysfunction, which can manifest as decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and decreased ejaculate volume. These effects have been observed in a minority of patients but warrant consideration.
Less Common Side Effects
Other side effects may include breast tenderness or enlargement, rash, and liver enzyme alterations. Although rare, some individuals report mood changes, including depression or anxiety. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers can help monitor these potential issues and adjust treatment as necessary.
Monitoring Recommendations
Monitor for any signs of adverse reactions. Maintaining open communication with your healthcare provider ensures timely management of any side effects. For patients considering or currently using Finasteride, tracking symptoms in a journal can support productive discussions during appointments.
| Potential Side Effect | Frequency | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
| Decreased libido | Common | Consult healthcare provider if persistent |
| Erectile dysfunction | Common | Discuss alternatives with your doctor |
| Breast tenderness/enlargement | Less Common | Seek medical advice for concerns |
| Mood changes | Rare | Reach out to support if experiencing symptoms |
Comparative Effectiveness of Finasteride vs. Alternative Treatments
Finasteride shows significant benefits in treating prostate inflammation, particularly for men with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Clinical studies indicate that it reduces prostate volume and alleviates urinary symptoms in about 70% of users within six months. Contrast this with alternative treatments such as alpha-blockers, which provide rapid symptom relief but may not address the underlying prostate enlargement effectively.
Herbal supplements like saw palmetto have gained popularity. Some research points to similar symptom reduction, yet results can be inconsistent, and they often take longer to show effects compared to finasteride. It’s essential to consider that saw palmetto lacks the regulatory approval and scientific backing found with finasteride.
Complementary therapies such as lifestyle changes, weight management, and physical activity can support overall prostate health. However, these measures alone have not demonstrated the ability to manage inflammation effectively. Combining these lifestyle adjustments with finasteride could enhance outcomes for many individuals.
For those hesitant to use medication, minimally invasive procedures, such as transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), may offer a mechanical solution to severe symptoms and inflammation. While these procedures provide immediate results, they carry risks of complications and longer recovery times compared to medication.
In a direct comparison, finasteride remains a robust choice for managing prostate inflammation, particularly for long-term therapy. For immediate symptom relief, alpha-blockers or other alternatives may be complementary options, but consultation with a healthcare provider is vital to tailor the treatment plan to individual needs. Combining approaches often yields the most balanced results, addressing both symptoms and root causes effectively.
Recommendations for Patients Considering Finasteride
Consult with your healthcare provider to discuss your medical history and examine any potential drug interactions. Understanding your unique health situation helps tailor treatment effectively.
Consider starting with a lower dosage. Many patients find that beginning with a smaller amount of finasteride reduces the likelihood of side effects while still providing benefits for prostate inflammation.
- Monitor Symptoms: Keep track of changes in urinary symptoms and overall prostate health. Document any improvements or side effects for your follow-up appointments.
- Follow Up Regularly: Schedule regular check-ups with your doctor to assess the treatment’s effectiveness and make necessary adjustments.
- Be Aware of Side Effects: Familiarize yourself with potential side effects, which may include sexual dysfunction, breast tenderness, or changes in mood. Report any concerns to your healthcare provider promptly.
Consider lifestyle modifications alongside medication. Increasing physical activity, maintaining a balanced diet, and managing stress levels can complement your treatment and promote better prostate health.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to support urinary function.
- Limit Alcohol and Caffeine: These substances can irritate the bladder and affect urinary symptoms.
- Discuss Alternatives: If finasteride isn’t suitable, explore other treatment options with your doctor. Medications or therapies may better align with your needs.
Share your concerns about fertility with your doctor. Finasteride may impact sperm production, and discussing these issues ensures you make informed decisions regarding future family planning.
Stay informed about ongoing research. New studies may provide insights into finasteride’s long-term effects, potential benefits, or alternative treatments that may arise.