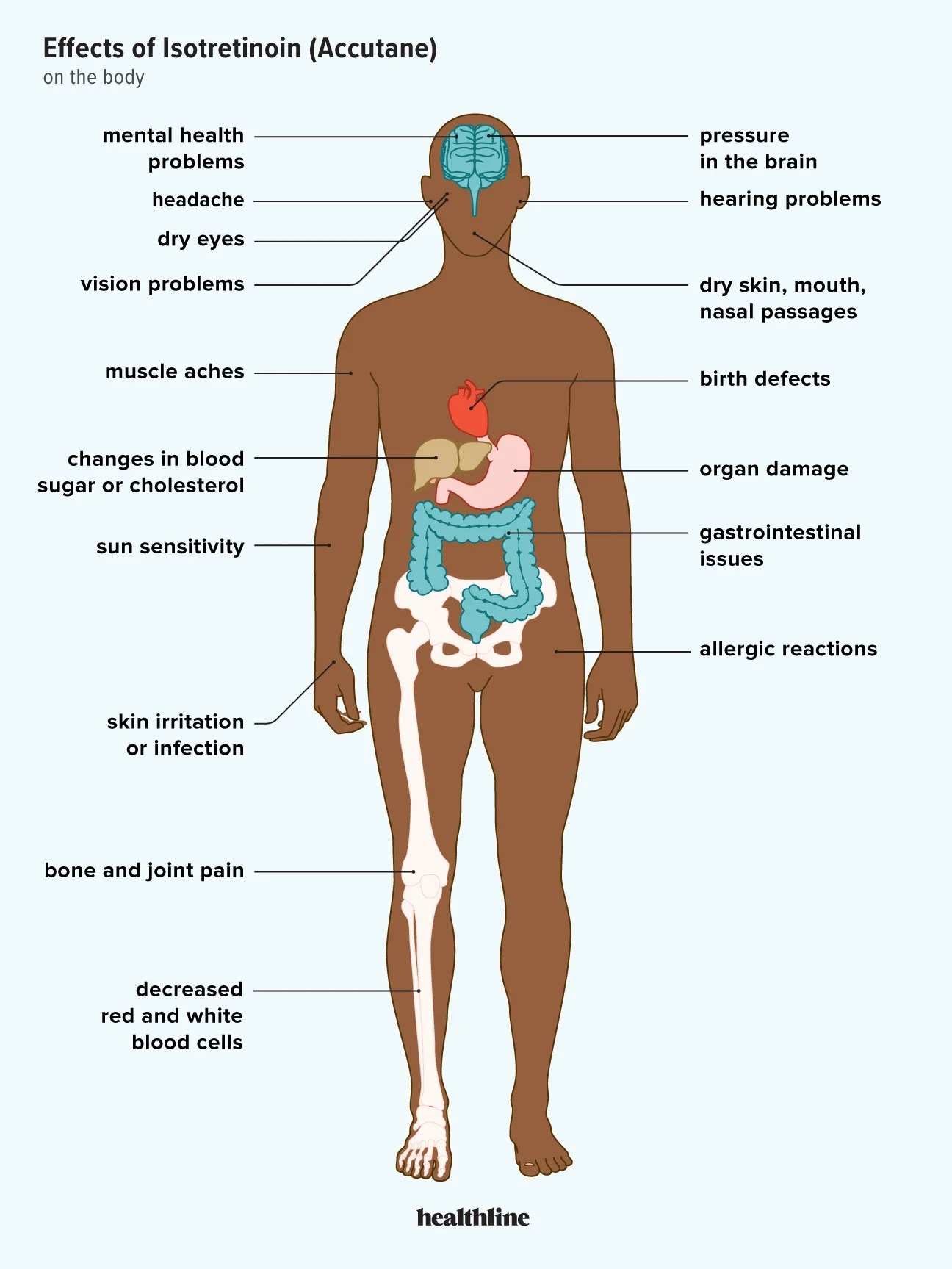
If you’re experiencing night sweats while on Accutane, it’s important to address this concern promptly. Night sweats can stem from various causes, and Accutane, known for its powerful effects on acne, may contribute to this discomfort. Consult your healthcare provider to understand if there’s a direct link between your medication and night sweats.
Night sweats can manifest as excessive sweating during the night, disrupting sleep and causing discomfort. On Accutane, which alters your body’s oil production and hormonal balance, some individuals report increased sensitivity to changes in temperature. Maintaining a cool sleeping environment and wearing breathable fabrics can help alleviate symptoms.
In addition to environmental adjustments, ensure you’re staying hydrated. Dry skin is a common side effect of Accutane, which can exacerbate feelings of overheating during the night. Incorporating a gentle moisturizer may help your skin adjust and improve overall comfort. Monitoring your diet can also play a role; spicy foods and caffeine may trigger or worsen night sweats.
Keep your doctor informed about your symptoms. They might recommend adjusting your dosage or exploring alternative treatments if night sweats persist. Tracking your experience will assist them in providing the best guidance tailored to your needs.
- Night Sweats and Accutane
- Understanding Night Sweats: Causes and Symptoms
- How Accutane Affects the Body’s Temperature Regulation
- Mechanism of Action
- Managing Temperature Regulation Issues
- The Connection Between Accutane and Night Sweats
- Understanding the Mechanism
- Managing Night Sweats
- Managing Night Sweats While on Accutane
- Stay Hydrated
- Monitor Your Diet
- When to Consult a Doctor About Night Sweats and Accutane
- When Symptoms Worsen
- After Starting New Medications
- Long-term Effects: Night Sweats After Discontinuing Accutane
- Understanding the Mechanism
- Management Strategies
Night Sweats and Accutane
If you experience night sweats while taking Accutane, consult with your healthcare provider promptly. Night sweats can be a side effect of this medication, affecting your sleep quality and overall comfort.
Here are several steps to address this issue:
- Monitor Your Symptoms: Keep a diary of your night sweats, noting their frequency and intensity. This information can help your doctor assess your situation better.
- Adjust Room Temperature: Maintain a cooler sleeping environment, possibly using fans or air conditioning to alleviate discomfort during the night.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink enough water throughout the day to maintain hydration. Dehydration may exacerbate sweating at night.
- Choose Appropriate Bedding: Use breathable fabrics for your sheets and pajamas. Cotton is a good choice as it allows for better airflow.
- Evaluate Your Diet: Avoid spicy foods, caffeine, and alcohol before bed, as these may contribute to increased sweating.
Your doctor may suggest adjusting your dosage or switching medications if night sweats persist. Collaboration with your healthcare provider ensures tailored solutions and proper management of any side effects.
Stay informed about potential side effects; understanding your body’s reactions can lead to better outcomes during your treatment with Accutane.
Understanding Night Sweats: Causes and Symptoms
If you experience night sweats, identifying potential causes can guide appropriate action. Hormonal changes often trigger these episodes, particularly during menopause. Fluctuations in estrogen levels can lead to increased body temperature at night.
Infections rank highly among causes, where conditions like tuberculosis or HIV/AIDS manifest through excessive sweating. Autoimmune disorders, such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, can also contribute to night sweats, as the body reacts to inflammation.
Medications might play a role too. Certain drugs, including antidepressants and fever-reducing medications, may induce sweat episodes. If you suspect a medication is the culprit, consulting a healthcare provider is wise.
Underlying health issues can lead to night sweats. Conditions like hyperhidrosis, where the body sweats excessively without a known cause, should be evaluated. Anxiety and stress can worsen this symptom, as they trigger the body’s fight-or-flight response.
Keeping track of additional symptoms, like fever, weight loss, or changes in appetite, is beneficial. These factors may indicate a more serious underlying condition requiring prompt medical attention. Regular discussions with a healthcare professional can clarify and address these symptoms effectively.
Maintaining a cool sleep environment can help ease the discomfort associated with night sweats. Wearing breathable fabrics and using fans or air conditioning may alleviate symptoms. Monitoring diet and reducing caffeine or alcohol before bedtime is recommended.
How Accutane Affects the Body’s Temperature Regulation
Accutane, or isotretinoin, can cause changes in the body’s ability to regulate temperature. Users may experience night sweats, which can be attributed to the drug’s effect on the sweat glands. This medication alters skin properties and may increase sweat production even during rest.
Mechanism of Action
Isotretinoin works by reducing oil production in glands, leading to drier skin, but it can paradoxically enhance sweating in some cases. The alteration of skin permeability and sweat gland activity can disrupt normal temperature regulation. As a result, individuals may find themselves sweating at night as the body struggles to maintain thermal balance.
Managing Temperature Regulation Issues
To alleviate night sweats, consider the following recommendations:
- Maintain a cool sleeping environment by using fans and breathable bedding.
- Wear loose-fitting, moisture-wicking sleepwear.
- Stay hydrated, as adequate fluid intake can help regulate body temperature.
| Strategy | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Cool sleeping environment | Reduces overall body temperature, minimizing sweat. |
| Loose-fitting sleepwear | Enhances airflow, decreasing moisture retention. |
| Hydration | Supports the body’s thermoregulation process. |
Discuss any persistent symptoms with your healthcare provider, as they may offer additional strategies or assess whether dosage adjustments are needed. Monitoring your body’s response while on Accutane is crucial for ensuring comfort and effectiveness during treatment.
The Connection Between Accutane and Night Sweats
Accutane, a powerful medication used for severe acne, can lead to various side effects, including night sweats. Increased sweating may occur due to the drug’s impact on the body’s regulatory mechanisms. This effect can cause discomfort, especially during sleep, disrupting rest and causing anxiety for some users.
Understanding the Mechanism
The active ingredient in Accutane, isotretinoin, alters sebaceous gland function and can affect skin hydration and thermoregulation. These changes may lead to hyperhidrosis, where the body produces excess sweat, particularly at night. This effect often coincides with other common symptoms linked to Accutane, such as dryness and irritation of the skin and mucous membranes.
Managing Night Sweats
If night sweats become problematic, consider adjusting your sleep environment. Keep the bedroom cool, use breathable bedding, and wear moisture-wicking clothing. Staying hydrated throughout the day can also help the body manage temperature fluctuations more effectively. If night sweats persist or worsen, consult your healthcare provider to discuss potential adjustments to your treatment plan or exploring coping strategies.
Managing Night Sweats While on Accutane
Adjust your sleeping environment to combat night sweats. Maintain a cool room temperature, ideally between 60-67°F (15-19°C), and use breathable bedding materials such as cotton or moisture-wicking fabrics. Opt for lighter pajamas to enhance comfort. Consider using a fan or air conditioning to circulate air and keep your sleeping area dry.
Stay Hydrated
Hydration plays a significant role in regulating body temperature. Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Herbal teas and electrolyte-rich drinks can also support your hydration levels. Avoid caffeine and alcohol, as they may exacerbate sweating episodes during the night.
Monitor Your Diet
Review your evening meals to minimize potential triggers for night sweats. Spicy foods, heavy meals, and foods high in sugar can increase body temperature. Focus on lighter dinners with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Keep an eye on your intake of foods that you may personally find challenging.
When to Consult a Doctor About Night Sweats and Accutane
If you experience night sweats while taking Accutane, consult a healthcare professional promptly. Document the frequency and intensity of the sweats, and consider any accompanying symptoms such as fever, fatigue, or weight loss. These details can help your doctor understand your condition better.
When Symptoms Worsen
Seek medical advice if night sweats become more frequent or severe. Significant changes in your body’s response can indicate an underlying issue that may need attention. If you notice a rash, increased heart rate, or shortness of breath, discuss these symptoms immediately with your doctor.
After Starting New Medications
If you start any new medications alongside Accutane, monitor for any signs of interaction or side effects. Inform your doctor about all medications you are taking. Night sweats could be a side effect of another drug, warranting an assessment of your treatment plan.
Long-term Effects: Night Sweats After Discontinuing Accutane
Night sweats can persist after stopping Accutane, a medication commonly used for severe acne. Many individuals report experiencing this side effect even months post-treatment. This occurrence may be linked to hormonal fluctuations caused by the drug, which alters sebum production and affects the body’s overall endocrine system.
Understanding the Mechanism
Accutane significantly reduces oil production in the skin, which can lead to changes in your body’s temperature regulation. As your body adjusts after discontinuation, it might experience imbalances that manifest as night sweats. Stress, hormonal changes, and even diet can contribute to this. Tracking your symptoms and their triggers can provide insight and help manage the situation.
Management Strategies
Staying cool during sleep can help. Consider using breathable fabrics for bedding and sleepwear. Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and practicing relaxation techniques may also alleviate symptoms. If night sweats persist beyond a few months, consulting a healthcare professional is advisable. They can evaluate other potential causes and recommend appropriate treatment if necessary.