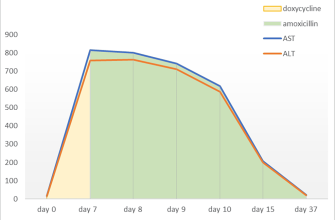
If you are prescribed ciprofloxacin, it’s important to understand how to take this medication correctly for optimal results. Ciprofloxacin is an antibiotic belonging to the fluoroquinolone class, commonly used to treat various bacterial infections such as urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, and skin infections. Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions precisely regarding dosage and duration.
Take ciprofloxacin with a full glass of water, and ensure you maintain adequate hydration throughout your treatment. This antibiotic can be taken with or without food, but consuming it with dairy products or calcium-fortified juices may impact absorption. If you experience any gastrointestinal upset, having it with food can help alleviate these symptoms.
Be aware of potential interactions with other medications. Certain antacids, supplements, or medications containing magnesium, aluminum, or zinc may hinder ciprofloxacin’s effectiveness. Space out the doses of these substances by at least two hours to ensure proper absorption of the antibiotic.
Monitor for side effects such as nausea, diarrhea, or dizziness, and report any unusual symptoms to your healthcare provider. With these guidelines, you can maximize the benefits of ciprofloxacin, reducing the risk of complications and contributing to a faster recovery from your infection.
- Prescription Ciprofloxacin
- Indications for Use
- Precautions and Interactions
- Understanding the Uses of Ciprofloxacin in Infectious Diseases
- Important Dosage Guidelines and Administration Techniques for Ciprofloxacin
- Dosage Recommendations
- Administration Techniques
- Potential Side Effects and Drug Interactions of Ciprofloxacin
Prescription Ciprofloxacin
Administer ciprofloxacin for bacterial infections when sensitivity testing confirms its efficacy. Typical dosages for adults range from 250 mg to 750 mg, taken every 12 hours. Adjust dosage for specific conditions such as urinary tract infections or respiratory infections based on severity and patient response.
Indications for Use
Prescribe ciprofloxacin primarily for urinary tract infections, certain gastrointestinal infections, and respiratory infections. Always confirm the diagnosis and ensure that the antibiotic aligns with culture and sensitivity results to maximize treatment outcomes.
Precautions and Interactions
Monitor for potential side effects, including gastrointestinal disturbances and central nervous system reactions. Avoid concurrent administration with certain medications like antacids or sucralfate, as these can interfere with absorption. Consider contraindications in patients with a history of tendon disorders related to fluoroquinolone use.
Understanding the Uses of Ciprofloxacin in Infectious Diseases
Ciprofloxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic widely used to treat various bacterial infections. It effectively targets Gram-negative bacteria, such as Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, making it a go-to choice for urinary tract infections (UTIs) and respiratory tract infections.
Healthcare providers often prescribe ciprofloxacin for conditions like pneumonia, especially in patients with risk factors for resistant strains. Additionally, it plays a role in treating skin and soft tissue infections, where timely intervention is critical to prevent complications.
In cases of complicated intra-abdominal infections, ciprofloxacin is frequently combined with metronidazole to enhance its efficacy against anaerobic bacteria. This combination improves outcomes in patients requiring hospitalization and aggressive treatment.
Gastrointestinal infections caused by Salmonella, Shigella, or Campylobacter can also benefit from ciprofloxacin therapy, particularly for those experiencing severe symptoms or prolonged illness. Rapid initiation of treatment can lead to quicker recovery and a reduction in transmission risk.
In certain instances, ciprofloxacin is employed as a preventive measure against infections, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy or with HIV/AIDS. It helps minimize the risk of bacterial infections during periods of vulnerability.
Resistance patterns require careful consideration before prescribing this antibiotic. Healthcare practitioners must assess local antibiograms to ensure ciprofloxacin remains an effective treatment option. Monitoring for potential side effects, including tendon rupture and neurological symptoms, is essential throughout the treatment process.
In summary, ciprofloxacin serves a significant role in managing a variety of infectious diseases, particularly those involving resistant bacteria. Its versatility and effectiveness make it an invaluable tool in modern medicine, though responsible prescribing practices are critical to maintaining its usefulness in clinical settings.
Important Dosage Guidelines and Administration Techniques for Ciprofloxacin
Follow these specific guidelines to ensure safe and effective use of ciprofloxacin:
Dosage Recommendations
- Standard adult dosage ranges from 250 mg to 750 mg, dependent on the type and severity of the infection.
- For urinary tract infections, a common dose is 250 mg every 12 hours for 3 days.
- For more serious infections, such as respiratory tract infections, you may need 500 mg every 12 hours for 7 to 14 days.
- Adjust dosages for patients with renal impairment; consult a healthcare provider for specifics.
Administration Techniques
- Swallow ciprofloxacin tablets whole with a glass of water; do not split or chew.
- Take ciprofloxacin on an empty stomach for optimal absorption; avoid taking it with dairy products or calcium-fortified juices within 6 hours before or 2 hours after doses.
- If prescribed liquid ciprofloxacin, shake the bottle well before each dose.
- Maintain adequate hydration throughout the treatment to help prevent crystalluria, especially in high doses.
Discuss any missed doses with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of action. Always follow your prescribed dosage carefully and report any severe side effects promptly.
Potential Side Effects and Drug Interactions of Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin may cause several side effects. Common reactions include nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and dizziness. Serious side effects can occur, including tendon rupture, changes in heart rhythm (QT prolongation), and central nervous system effects such as seizures or increased intracranial pressure. If experiencing severe side effects, seek medical attention immediately.
Alongside these potential adverse effects, monitor for interactions with other medications. Ciprofloxacin can interact with various drugs, impacting their effectiveness or increasing side effects. The following table outlines notable drug interactions:
| Drug Category | Interaction Type | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Antacids | Reduce absorption | Avoid taking within 2 hours of ciprofloxacin. |
| Warfarin | Increased bleeding risk | Monitor INR levels closely. |
| NSAIDs | Increased risk of CNS effects | Exercise caution; consider alternatives. |
| Diabetes medications | Possible hypoglycemia | Monitor blood glucose levels regularly. |
| Other QT-prolonging agents | Increased risk of arrhythmias | Avoid concurrent use if possible. |
Always inform your healthcare provider about all medications taken, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to minimize risks. Regular check-ups allow for timely adjustments to the treatment plan, ensuring safety and effectiveness.