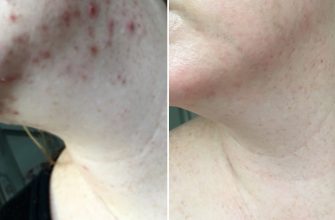
If you’re grappling with alopecia areata and considering treatment options, Rogaine (minoxidil) could offer a path to hair regrowth. This topical solution has shown promise in helping to restore hair for some individuals, particularly when used consistently over time. Clinical studies have indicated that Rogaine can stimulate hair follicles and promote regrowth, especially in cases of patchy hair loss.
When using Rogaine, apply the solution directly to the affected areas twice daily. It’s essential to follow the dosing instructions carefully to achieve optimal results. The formulation is available in both liquid and foam, allowing you to choose what feels most comfortable and convenient for you.
Initial hair regrowth may take several weeks, and it’s common for users to experience shedding before seeing new growth. This process indicates that the follicles are responding to the treatment. Monitor your progress over the first three to six months to determine if Rogaine is beneficial for your specific situation.
Consulting with a healthcare provider before starting Rogaine is advisable to ensure it aligns with your overall treatment plan. With dedication and the right approach, Rogaine can be a valuable option in managing the symptoms of alopecia areata.
- Rogaine for Alopecia Areata
- How to Use Rogaine
- Potential Benefits and Considerations
- Understanding Alopecia Areata: Symptoms and Causes
- What is Rogaine and How Does It Work?
- Mechanism of Action
- Usage and Recommendations
- Efficacy of Rogaine for Treating Alopecia Areata
- Application Guidelines
- Combination Treatments
- Application Guidelines for Rogaine in Alopecia Areata
- Best Practices
- Monitoring Progress
- Potential Side Effects of Rogaine for Hair Loss
- Combining Rogaine with Other Treatments for Alopecia Areata
- Use of Anthralin and Rogaine
- Oral Medications and Rogaine
- Patient Experiences: Success Stories and Challenges with Rogaine
- Success Stories
- Challenges Faced
Rogaine for Alopecia Areata
Rogaine (minoxidil) is a topical treatment that can stimulate hair regrowth in individuals with alopecia areata. Its application can lead to visible improvements for some users, though results may vary.
How to Use Rogaine
- Apply Rogaine to dry hair and scalp twice daily.
- Use the provided applicator for precise application.
- Wash hands thoroughly after application to avoid unintended transfer.
- Allow the solution to dry completely before using any styling products.
Potential Benefits and Considerations
- Regular use may enhance hair thickness and growth within weeks.
- Side effects like scalp irritation or unwanted facial hair may occur.
- Consult a healthcare provider before starting, especially for underlying conditions.
- Patience is key; it may take several months to notice significant changes.
Maintaining consistency in application is crucial for achieving optimal results with Rogaine. Tailoring your expectations and understanding that individual response can differ will help in managing treatment effectively.
Understanding Alopecia Areata: Symptoms and Causes
Alopecia areata manifests primarily through hair loss. Recognizing its symptoms can lead to quicker management options.
- Patchy Hair Loss: The most common symptom is one or more round patches of hair loss on the scalp, face, or body.
- Unexplained Hair Loss: Sudden, hair loss can occur without noticeable signs, often leading to shock for those affected.
- Texture Changes: The remaining hair may become brittle or change texture before falling out.
- Nail Changes: Users may notice ridges, pitting, or other abnormalities in their nails.
Understanding the causes aids in addressing alopecia areata effectively. It stems from an autoimmune response where the body mistakenly attacks hair follicles. Factors contributing to this condition include:
- Genetic Disposition: A family history of autoimmune diseases increases susceptibility.
- Environmental Triggers: Certain infections, stressors, or traumatic events can precipitate hair loss.
- Immune System Dysregulation: An imbalance in immune response plays a significant role in the development of alopecia areata.
Prompt identification supports better management options. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and potential treatment pathways.
What is Rogaine and How Does It Work?
Rogaine, containing the active ingredient minoxidil, is a topical treatment primarily used for hair loss. It stimulates hair follicles, promoting hair regrowth and slowing down further loss. Applied directly to the scalp, it helps improve blood circulation in the area, delivering essential nutrients to hair roots. This process strengthens existing hairs and encourages new growth.
Mechanism of Action
Minoxidil acts as a vasodilator, widening blood vessels. This increased blood flow to the hair follicles enhances their function, leading to the revitalization of shrunken hair follicles. Over time, patients can observe a transition from thin, short hair to thicker, longer strands. Regular application is crucial, as discontinuing treatment can reverse these benefits.
Usage and Recommendations
Apply Rogaine twice daily, following the instructions on the product label or your healthcare provider’s advice. Consistency is key; improvements typically appear after several months. Monitor your scalp for any irritation or side effects, and consult a doctor if needed. It’s advisable to use Rogaine in conjunction with other treatments for increased efficacy in managing alopecia areata.
Efficacy of Rogaine for Treating Alopecia Areata
Rogaine, known generically as minoxidil, shows promise for individuals facing alopecia areata. Clinical studies indicate varying degrees of effectiveness, highlighting a response rate between 30% to 50% for users in the short term. Optimal results often occur when treatment begins early after onset.
Application Guidelines
Apply Rogaine directly to the scalp twice daily. Consistency in application is crucial. Most users see initial hair regrowth within two to four months. Patience is key, as results can take time to manifest. Always follow the instructions provided on the label and consult a healthcare provider if experiencing any adverse reactions.
Combination Treatments
Combining Rogaine with corticosteroids can enhance outcomes. Corticosteroids help reduce inflammation associated with alopecia areata and may boost the effectiveness of minoxidil. Discuss this option with a dermatologist to tailor the treatment to your specific needs.
While Rogaine is not a guaranteed solution, many patients report satisfactory results. Monitoring progress and adjusting the treatment plan with professional guidance leads to optimal regrowth opportunities.
Application Guidelines for Rogaine in Alopecia Areata
Apply Rogaine directly to clean, dry scalp areas affected by alopecia areata. Use the recommended dosage of 1 mL twice daily. Ensure the scalp is fully dry before application to optimize absorption. Avoid rinsing for at least four hours post-application to enhance efficacy.
Best Practices
Before using Rogaine, wash your hands thoroughly. Part your hair to expose the affected areas, then use the dropper to dispense the solution. Gently massage the product into the scalp, focusing on regions with hair loss. Do not use excessive amounts; more does not increase benefits and may lead to irritation.
Monitoring Progress
Track your results over time. Visible improvements may take several weeks, often appearing around 12 weeks into consistent use. Document any side effects like itching or redness; if persistent, consult a healthcare professional. Regular application at the same times enhances adherence and maximizes outcomes.
Potential Side Effects of Rogaine for Hair Loss
Users of Rogaine (minoxidil) should be aware of potential side effects that may arise during treatment. Common reactions include skin irritation, such as redness or itching at the application site. This generally subsides as your skin adjusts. However, persistent irritation may require discontinuation of the product.
Some individuals experience unwanted facial hair growth. This occurs when the medication spreads to unintended areas or when hair follicles are stimulated in sensitive regions. If this happens, adjusting the application technique can help minimize the spread.
In rare cases, users report dizziness or lightheadedness, especially after standing up quickly. This effect is usually temporary but should not be ignored, particularly if it leads to falls or injuries. Staying hydrated can alleviate this symptom.
Changes in hair texture may occur as new hair grows in. You might notice these new hairs are finer or different in appearance compared to your existing hair. These changes are typically normal and part of the hair regrowth cycle.
Allergic reactions are infrequent but can happen. Symptoms such as swelling, rash, or difficulty breathing require immediate medical attention. Cease using Rogaine and consult a healthcare provider if you notice these signs.
Frequent use of Rogaine does not guarantee continued effectiveness. If hair loss resumes after stopping treatment, consider discussing alternative options with a dermatologist. Regular follow-ups can ensure suitable management of both side effects and hair regrowth strategies.
Staying informed about these potential side effects can enhance your experience with Rogaine and contribute to successful management of hair loss. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting or adjusting your treatment regime.
Combining Rogaine with Other Treatments for Alopecia Areata
Using Rogaine (minoxidil) in conjunction with other therapies can enhance results in managing alopecia areata. Combining Rogaine with corticosteroids often yields significant improvements. Topical corticosteroids can reduce inflammation and promote hair regrowth. Apply minoxidil after the steroid treatment for optimal absorption and efficacy.
Use of Anthralin and Rogaine
Another effective combination includes anthralin, a topical medication that modifies immune response. When used with Rogaine, it can boost hair regrowth. Start with anthralin application for a few hours, then rinse off and follow with Rogaine. This method harnesses both the immunomodulatory effects of anthralin and the stimulatory properties of minoxidil.
Oral Medications and Rogaine
Incorporating oral treatments like corticosteroids or JAK inhibitors can enhance results as well. JAK inhibitors target the immune pathways involved in alopecia areata. Administer these medications under medical supervision while continuing Rogaine. This combination can facilitate more substantial hair restoration for those with extensive or recalcitrant cases.
Patient Experiences: Success Stories and Challenges with Rogaine
Patients frequently report significant improvements after incorporating Rogaine into their treatment for alopecia areata. For many, visible results appear within 4 to 6 months. Regular application drastically enhances hair regrowth in treated areas. Maintaining a consistent routine is pivotal for achieving desired outcomes.
Success Stories
One user shared, “I noticed thicker hair within just two months. The patches that were once bare began filling in nicely.” Another patient emphasized the emotional boost: “Seeing my hair grow back gave me confidence I thought I lost.” Rogaine appears to stimulate hair follicles effectively. Some users even noted that combining Rogaine with other therapies, such as corticosteroid injections, accelerated their progress.
Challenges Faced
Despite positive experiences, not all patients see immediate benefits. A user mentioned, “I faced a few setbacks during my treatment. There were phases when I experienced increased shedding.” This phenomenon can occur as hair follicles transition, which is a natural response. Consulting with a healthcare provider during these challenging moments can help manage expectations and adjust treatment plans.
| Experience Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Positive Response | Visible hair regrowth within 4-6 months |
| Emotional Impact | Increased confidence and satisfaction |
| Setback | Initial increased shedding before improvement |
| Combination Therapy | Enhanced results with additional treatments |
Individual results vary, emphasizing the need for personalized treatment plans. The stories highlight a balance of hope and realism that can guide others considering Rogaine for their alopecia areata journey.